Condyloma Acuminatum is a skin condition where non-carcinogenic (noncancerous) skin tumors form due to exposure to the HPV papillomavirus. We usually see the condyloma in the groin, cervix, vagina, penis, and sometimes in the anal cavity. In rare cases, they can appear on the lips, mouth, throat, and tongue.
As mentioned, condyloma is caused by the HPV virus, one of the world’s most well-known and common venereal diseases.
In adults, it is almost always spread through sexual contact. However, it can appear in children; although rare, it can pass during pregnancy or even during childbirth.
What are the common symptoms of Condyloma?
Flat moles that were not present before appearing on the skin.
Warts cluster together, sometimes resembling cauliflower.
Discomfort or itching in the genital region.
Thick discharge or bleeding during sexual intercourse
How do we diagnose Condyloma? (Dr. Google is not a board certified doctor!)
The diagnosis generally requires a visual examination of the genital region. If you’re doubtful, it is best to schedule a gynecological exam + Pap and to have the biopsy sent to a lab.
A colposcopy is another method; it is a simple procedure to examine the cervix more clearly than the naked eye.
An HPV test is another method, sending a sample to a lab to identify the strain.
How are lesions treated?
The following treatments are what is currently available in treating Condyloma
- Freezing warts with liquid nitrogen
- Laser treatments
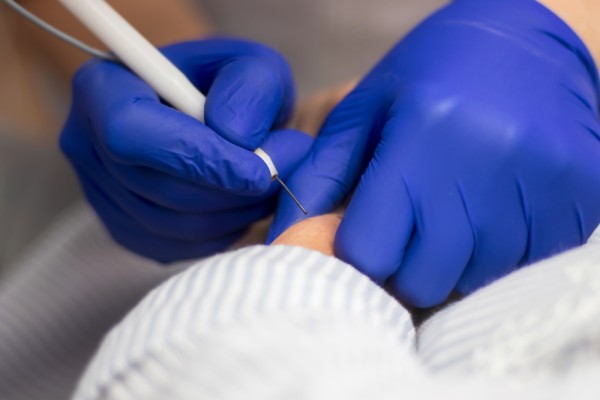
- Electric needle
- Lotion and/or ointments
- Excision
Laser Treatment of Condyloma
Today, the most common method of removing Condyloma is through laser treatments. The laser destroys the blood vessels in and around warts, using the high temperature of the laser. Without these blood vessels, warts cannot continue to survive; therefore, they die. Usually, the doctor will use an anesthetic on the area before treatment. You may feel discomfort in the days following laser therapy. It is important to note that laser treatments can sometimes leave scars- which usually heal over time, but it does not promise to eliminate future breakouts.
Low and High Risk
The strains are generally categorized as high and low risk
The strains defined as low risk usually cause the appearance of warts, the most common being 6 and 11. In total, in this family are the following strains: 6,11,42,43,44.
The strains defined as high risk are 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45 ,51, 52. Strains 16 and 18 are primarily responsible for malignant changes to the cervix.
Why is it so important that women get their Pap tests in an organized fashion?
It is essential to get a Pap smear because external symptoms like warts, itching, or bleeding often do not appear. In addition, it means someone can be exposed to the virus and not be aware of it.
A Pap test detects inflammatory cells formed as a result of exposure to the virus.

Dr. Guy Gutman
A senior physician at the Clalit Health Women’s Center, a specialist in gynecology and cervical medicine, with 20 years of successful experience in infertility, obstetrics, and gynecology.